The X Theory and the Y TheoryMcGregor promoted Theory Y as the basis of good management practice pioneering the argument that workers are not merely cogs in the company machinery as Theory X-Type organizations seemed to believe. Rather he saw the two theories as two extremes - with a whole spectrum of possible behaviours in between.
 Theory X And Theory Y Of Motivation By Mcgregor
Theory X And Theory Y Of Motivation By Mcgregor
Theory X and theory y are considered as theories of human motivation at the workplace.

Theory x and theory y by mcgregor. Business Management Leadership No Result. They were created by Douglas McGregor while he was working at the MIT Sloan School of Management in the 1950s and developed further in the 1960s. For example if you think that your team members do not like their work and have a lack of interest andor motivation then according to McGregor theory you are required to use the Authoritarian Theory X style of management.
Theory Y is an advanced theory wherein it is assumed that the workers are self-directed and self-motivated for growth and development and takes active part in decision making. McGregor observed that X-type workers are in fact mostly in minority and yet in mass organizations such as large scale production environment X Theory management may be needed and can be unavoidable. One of which is negative called as Theory X and the other is positive so called as Theory Y.
Both theories X and Y are proposed by McGregor which describe the workforce models which are contrasting in nature and which are used by reporting managers in organizational behaviour and human. However he found that an organisation. Theory into practice Abraham Maslow viewed McGregor as a mentor.
This theory is very common and includes micromanaging peoples work to make sure that it is done properly. This is an example of a content theory of motivation. McGregors Theory X and Theory Y.
The Theory X management style is based on a pessimistic view of human nature. Motivation - McGregor Theory X Theory Y McGregor developed two theories of human behaviour at work. Theory X Theory Y.
How are McGregors Theories X and Y and Ouchis Theory Z used to explain worker motivation. According to theory X there are following assumptions about human nature on which the manager has to base his motivation efforts. Douglas McGregor then arrived at the conclusion that the style of leadership depends on the managers perception of people.
McGregors Theory X and Theory Y is a theory for human management and human work motivation. The idea that a managers attitude has an impact on employee motivation was originally proposed by Douglas McGregor a management professor at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology during the 1950s and 1960sIn his 1960 book The Human Side of Enterprise McGregor proposed two theories by which managers perceive and address employee motivation. In 1960 Douglas McGregor formulated Theory X and Theory Y suggesting two aspects of human behaviour at work or in other words two different views of individuals employees.
In 1960 Douglas McGregor developed a leadership theory McGregor Theory X and Theory Y about organization and management in which he represented two opposing perceptions about people. McGregors work was rooted in motivation theory alongside the works of Abraham Maslow who created the hierarchy of needs. He referred to these opposing motivational methods as Theory X and Theory Y management.
The Definitive Guide Step-by-Step Maslows Hierarchy of Needs. The average human being has an inherent dislike of work and will avoid it if he can do so. Douglas McGregor one of Maslow s students influenced the study of motivation with his formulation of two contrasting sets of assumptions about human nature Theory X and Theory Y.
These assumptions which he called Theory X and Theory Y are implicit in most approaches to supervision. This theory explains a participative style of management that is distributive in nature. 76 McGregors Theories X and Y.
He referred to these two perceptions as Theory X and Theory Y. Theory X and Theory Y. McGregors sets forth two alternative views of human nature first view are called Theory-X and the second view is called Theory-Y.
These theories are based on the premise that management has to assemble all the factors of production including human beings to get the work done. These have been represented by Theory X and Theory Y. Theory and X and Theory Y.
The Theory X and Theory Y are the theories of motivation given by Douglas McGregor in 1960s. McGregors Theory X and Y. Each assumes that the managers role is to organize resources including people to best benefit the company.
Theory X is a motivational theory which involves high supervision and control over the subordinates and greater degree of centralization. According to McGregor the perception of managers on the nature of individuals is based on various assumptions. Theory X and Theory Y are theories of human work motivation and management.
He was a strong supporter of Theories X and Y and he put Theory Y that people want to work achieve and take responsibility into practice in a Californian electronics factory. This theory was developed by Douglas McGregor in 1950s at MIT. He did not imply that workers would be one type or the other.
These theories are opposite ends of a continuum. In his 1960 book The Human Side of Enterprise McGregor proposed two theories by which managers perceive and address employee motivation. The two theories proposed by McGregor describe contrasting models of workforce motivation applied by managers in human resource management organizational.
Theory X and Y of Human motivation was developed in the 1960s by Douglas McGregor an American social psychologist. I The average person dislikes work and whenever possible will avoid it ii Most people are not ambitious have little desire for responsibility and prefer to be directed. 5 Levels Features Difference.
McGregor presented two opposite sets of assumptions made by managers about their staff. X and consider using the techniques suggested by Theory Y. Social psychologist McGregors Theory-X and Theory-Yof MIT expounded two contrasting theories on human motivation and management in the 1960s.
Douglas McGregor has presented two opposite sets of assumptions about employees.
The Maslow motivation theory is one of the best known and most influential theories on workplace motivation. According to Maslow these needs.
.jpg) Maslow S Hierarchy Of Needs Simply Psychology
Maslow S Hierarchy Of Needs Simply Psychology
April 1 1908 June 8 1970 was an American psychologist who was best known for creating Maslows hierarchy of needs a theory of psychological health predicated on fulfilling innate human needs in priority culminating in self-actualization.
Explain abraham maslow theory of motivation. These needs are arranged in a hierarchy. This is a theory of psychological health predicated on fulfilling innate human needs in priority culminating in self-actualization. According to humanist psychologist Abraham Maslow our actions are motivated in order to achieve certain needs.
Psychologist Abraham Maslow first developed his famous theory of individual development and motivation in the 1940s. Maslows hierarchy needs theory of motivation clearly states that a person is motivated from an unsatisfied need only till the time it gets satisfied. They act to fulfill basic survival needs before addressing more advanced needs or wants.
Abraham Maslows motivation theory is based on the human needs. Probably the most widely known theory of individual need and motivation comes from Abraham Maslow who was a clinical psychologist in USA Maslow. The basis of Maslows theory of motivation is that human beings are motivated by unsatisfied needs and that certain lower needs need to be satisfied before higher needs can be addressed.
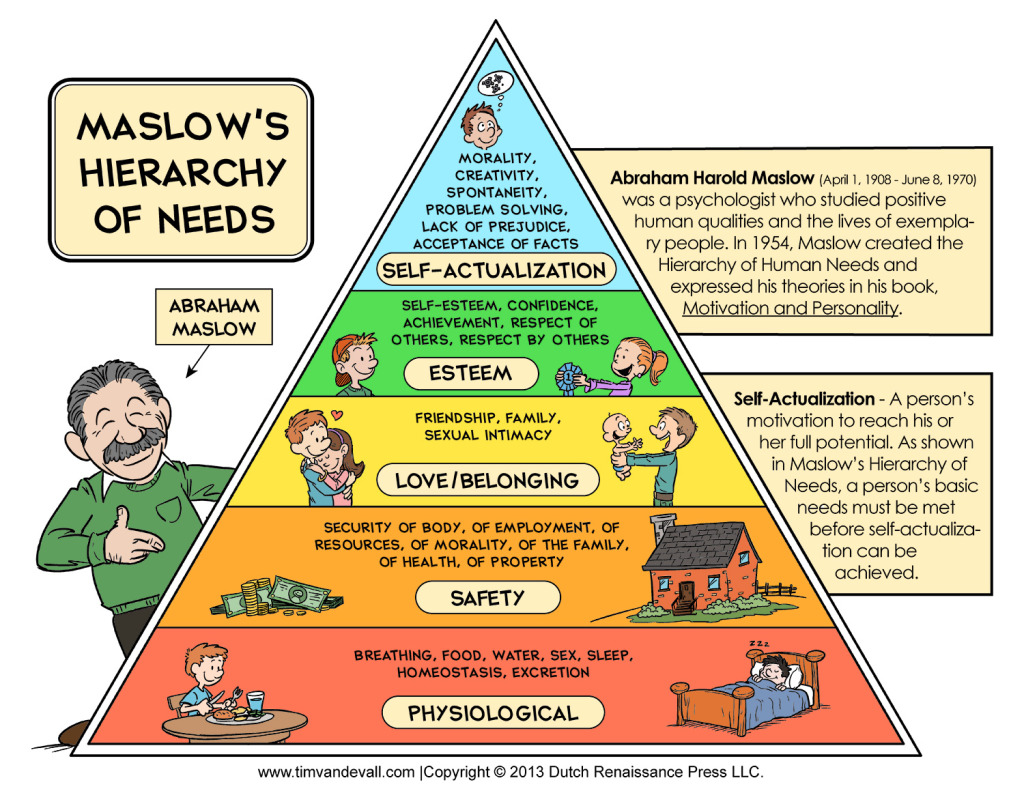
Physiological food and clothing safety job security love and belonging needs friendship esteem and self-actualization. Maslow proposed that motivation is the result of a persons attempt at fulfilling five basic needs. Abraham Harold Maslow ˈmaezloʊ.
What is Maslows Hierarchy of Needs Theory. From the bottom of the hierarchy upwards the needs are. Abraham Maslows theory of motivation asserts that humans are motivated by a hierarchy of needs.
Maslow suggests that we seek first to satisfy the lowest level of needs. Maslows Hierarchy of Needs. He suggested that human beings have a hierarchy of needs.
He put further a theory that there are five levels in a hierarchy of human needs that employees require having satisfied at work. These needs are classified into a sequential hierarchy from the lower to higher order as five need clusters as shown in the following Figure 102. The above five need-clusters are now discussed in seriatim.
It is something that stimulates an individual to keep doing the act already initiated. Maslows hierarchy of needs is a theory in psychology proposed by the American psychologist Abraham Maslow in his 1943 paper A Theory of Human Motivation. This hierarchy ranges from more concrete needs such as food and water to abstract concepts such as self-fulfillment.
Maslows Hierarchy of Needs. Maslows believes that the lower level needs have to be satisfied before higher needs can influence behavior. Physiological safety social esteem and self-actualization.
Maslows Need Hierarchy Theory of Motivation Abraham Maslows research was actually focused on human personality and he suggested that people differ because they differ in their needs and motivation. In 1943 he published a paper called A Theory of Human Motivation in which he first presented his hierarchy of needs theory. Abraham Maslow is well renowned for proposing the Hierarchy of Needs Theory in 1943.
This hierarchy is shaped like a pyramid with the lower levels occupied by physical physiological needs such as food water and shelter. Maslows Need Hierarchy Theory of Motivation. This hierarchy suggests that people are motivated to fulfill basic needs before moving on to other more advanced needs.
In order to better understand what motivates human beings Maslow proposed that human needs can be organized into a hierarchy. In this context Abraham Maslow a renowned psychologist highlighted the elements of the theory of motivation in a classic paper released in 1943. Maslow grouped human needs into five categories.
This theory is a classical depiction of human motivation. Maslow first introduced his concept of a hierarchy of needs in his 1943 paper A Theory of Human Motivation and his subsequent book Motivation and Personality. Motivation implies the process of encouraging people to act in order to attain the desired objectives.
These needs will not motivate a person after he or she reaches to the next level. The urgency of these needs varies. That is that all humans act in a way which will address basic needs before moving on to satisfy other so-called higher level needs.
Maslows hierarchy of needs is a motivational theory in psychology comprising a five-tier model of human needs often depicted as hierarchical levels within a pyramid. Abraham Maslow 1908 - 1970 was a psychology professor who founded the Humanistic Psychology discipline. Hierarchy of needs theory summary.
The psychologist Abraham Maslow developed a theory that suggests we humans are motivated to satisfy five basic needs. He suggested that every individual has a complex set of exceptionally strong needs and the behaviour of an individual at a particular moment is usually determined by his strongest need. This theory is based on the assumption that there is a hierarchy of five needs within each individual.
Maslows hierarchy of needs is a motivational theory in psychology comprising a five-tier model of human needs often depicted as hierarchical levels within a pyramid.
What nontechnical term does Judee Burgoon use in reference to communication theory. Hunches that communication theory are built about should be A.
 Chapter 1 337 Rtf Full File At Http Testbanksinstant Eu Test Bank For A First Look At Communicationtheory 8th Ed By Em Griffin C1 Student Course Hero
Chapter 1 337 Rtf Full File At Http Testbanksinstant Eu Test Bank For A First Look At Communicationtheory 8th Ed By Em Griffin C1 Student Course Hero
Chapter 1 Hunches that communication theory are built about should be A.

Hunches that communication theory are built about should be. Regarding the use of theory versus intuition in therapy sessions Fox thinks counselors should strive for a combination of both. An umbrella term for all careful systematic and self-conscious discussion and analysis of communication phenomena. The use of gut hunches can be particularly useful in situations where a decision is needed and not all the information is present.
Theories always involve an element of speculation or conjecture. Should reflect commonly held beliefs d. Hunches that communication theory are built about should be.
All of the above. Hunches that communication theory are built about should be a. Go beyond accepted wisdom c.
Go beyond accepted wisdom. Kramarae believes men have difficulty understanding womens communication because. A set of systemic hunches about the way things operate 7.
Umbrella term for all careful systematic and self-consciousness discussion and analysis of communication phenomena p2. Theory in general and of communication theory in particular b trace the development of theoretical inquiry in the field of communication c evaluate the utility of theory by applying specific criteria and standards d. Which of the following was not posed as a metaphor for theories.
Alexa hunches is a feature that better understands your routines and suggests things to you. Hunches that communication theory are built about should be Open Homework Posted by. Hunches that communication theory are built about should be.
Alter what we already believe. Alter what we already believe b. 2 Day 3 writers want to do this homework.
Go beyond accepted wisdom. Which of the following was not posed as a metaphor for theories. Full file at Test-Bank-for-A-First-Look-at-Communication-Theory-8th-ed-By-Em-Griffin-4.
All of the above. All of the above. All of the above download full file at.
So for example if you tell Alexa youre about to go to bed itll. The critical theories paradigm proposes that we should strive to understand how communication may be used to exert power and oppress people. Which of following was no posed a metaphor for theories.
Set of systematic informed hunches about the way things work p3. Hence Taylor proposed that managers need to discard following their hunches and heuristics. Is the relational process of creating and interpreting messages that elect a response.
Infrormed plural and systematic- all of the above. A theory is a set of systematic informed hunches about the way things work Griffin 2012. Should reflect commonly held beliefs d.
Nets cast to catch what we call the world D. What is a Theory and What does it Do. All of the above.
The critical theories paradigm. Mirrors _____ is the relational process of creating and interpreting messages that elicit a response. Bthey havent made the effort to find out about it.
This knowledge helps to develop self-awareness and also to help others to achieve greater self-awareness and development too. Go beyond accepted wisdom. Alter what we already believe.
All of the above. This section seeks to explain many of these personality theories and ideas. Respond to at least two of your peers for this posting.
A theory is not just one inspired thought or an isolated idea. Theory gives practitioners a guiding framework from which to work but counselors should simultaneously seek information that comes from assessments and the counselors experience or intuition he says. A Foss S.
Go beyond accepted wisdom c. Usually violate or contradict accepted wisdom. How have you used either of the two theories in daily life.
Infrormed plural and systematic- all of the above. What nontechnical term does Judee Burgoon use in reference to communication theory. Should reflect commonly held.
Hunches that communication theory are built about should be A. Mirrors ____ is the relational process of creating and interpreting messages that elicit a response. Usually violate or contradict accepted wisdom.
DAll of the answers are correct. Hunches that communication theory are built about should be. Hunches that communication theory are built about should be A.
Set of hunches If a theory is a set of hunches it means we arent yet sure we have the answer. All of the above Griffin - Chapter 01 4 5. Launching your Study of Communication Theory Pages 1 12 4.
Hunches that communication theory are built about should be. Should we simply analyze and describe the ways in which groups communicate or should we challenge those ways and propose others. Describe the similarities and differences between the ERG Theory and Maslows Hierarchy.
Alter what we already believe b. Go beyond accepted wisdom. The personality theories that underpin personality tests and personality quizzes are surprisingly easy to understand at a basic level.
Discarding the rule of thumb would also imply that there would be considerable standardization of working protocols. Go beyond accepted wisdom. All of the above.
Relational process of creating and interpreting messages that elicit a response. Instead they need to be up-to-date with the latest scientific discoveries. All of the above 5.
This is because gut hunches are not based off of specific. Hunches that communication theory are built about should be. Hunches that communication theory are built about should be a.
Employee does not like to work and avoids work. Quite a few organizations use Theory X today.
 Mcgregor Theory X Theory Y Motivation Theory Organizational Behavior Industrial And Organizational Psychology
Mcgregor Theory X Theory Y Motivation Theory Organizational Behavior Industrial And Organizational Psychology
Introduction to McGregors Theory X and Theory Y.

Mcgregor xy theory definition. Most people are not ambitious have little desire for responsibility and prefer to be directed. His ideas suggest that there are two fundamental approaches to managing people. Definition of Theory Y Theory Y is a modern approach on motivation put forward by McGregor.
What is Theory X and Theory Y. Thus he encouraged cordial team relations responsible and stimulating jobs and participation of all in decision-making process. Douglas McGregor has developed two sets of assumptions about human behaviour.
These theories are based on the premise that management has to assemble all the factors of production including human beings to get the work done. The expenditure of physical and mental efforts in work is as natural as play or rest. - Ordinary people who do not dislike work.
The theories look at how a managers perceptions of what motivates his or her team members affects the way he or she behaves. The idea behind using letters X and Y perhaps seems to be using a neutral terminology which does not convey any sense of badness or goodness associated with these theories. The concept of Theory X and Theory Y was developed by social psychologist Douglas McGregor.
McGregors Theory X and Theory Y are theories about human behavior and motivation in the organization that was published in 1960 by Douglas McGregor. Work is inherently distasteful to most people and they will attempt to avoid work whenever possible. Theory y is McGregors other modem view of the nature of man.
McGregors work was rooted in motivation theory alongside the works of Abraham Maslow who created the hierarchy of needs. The two theories proposed by McGregor describe contrasting models of workforce motivation applied by managers in human resource management organizational. The Theory X management style is based on a pessimistic view of human nature and assumes the following.
Theory X encourages use of tight control and supervision. The average person dislikes work and will avoid it if possible. It contains assumptions which he believed could lead to greater motivation And better fulfillment of both individual needs and organizational goals.
The Theory X and Theory Y are the theories of motivation given by Douglas McGregor in 1960s. - Individuals who seek responsibility if they are motivated0. Managers assumptions about the behaviour of people are central to this.
McGregor argued that these assumptions fall into two broad categories - Theory X and Theory Y. This theory explains a participative style of management that is distributive in nature. It describes two contrasting sets of assumptions that managers make about their people.
McGregor promoted Theory Y as the basis of good management practice pioneering the argument that workers are not merely cogs in the company machinery as Theory X-Type organizations seemed to believe. McGregor views Theory Y to be more valid and reasonable than Theory X. Theory X and Theory Y were part of McGregors philosophy of management which represented a fundamental change in management thought and practice.
Theory X and Theory Y are theories of human work motivation and management. It uses the participative style of management and assumes that workforce is self-directed and enjoy the work assigned to them in the accomplishment of organisational objectives. McGregors X-Y theory is a salutary and simple reminder of the natural rules for managing people which under the pressure of day-to-day business are all too easily forgotten.
This theory divides workers and managers in the organization in two typical groups according to how managers lead their subordinates and respectively how subordinates behave. Depending on the working conditions work could be considered a source of satisfaction or punishment. Theory Y workers were characterised by McGregor as.
McGregor believed that managers basic beliefs have a dominant influence on the way that organisations are run. According to McGregor Theory X management assumes the following. Implications of Theory X and Theory Y.
The Assumptions of Theory Y Are. Many managers tend toward Theory X and generally get poor results. Labelling these as Theory X and Theory Y.
- Consider effort at work as just like rest or play. In 1960 Douglas McGregor developed a leadership theory McGregor Theory X and Theory Y about organization and management in which he represented two opposing perceptions about people. McGregor observed that X-type workers are in fact mostly in minority and yet in mass organizations such as large scale production environment X Theory management may be needed and can be unavoidable.
Theory X people dislike work have little ambition and are unwilling to take responsibility. Theory X and Theory Y definition Theory X and Theory Y developed by MIT management professor Douglas Murray McGregor are theories of human motivation that provide a framework for how managers use behaviours and tools in the workplace to encourage productivity. Because people dont like to work they must be controlled directed or threatened with punishment to get them to make an effort.
His major writings are cited along with two volumes which were actually published several years after his death by Bennis Caroline McGregor and Schein. They were created by Douglas McGregor while he was working at the MIT Sloan School of Management in the 1950s and developed further in the 1960s. Character of the manager or worker corresponding to the theory X.
These remarks may characterize the choice of the terms introversion and extraversion sufficiently enough so that we will be able to use them in further discussions. Extraversion and Introversion are the only terms amongst CG.
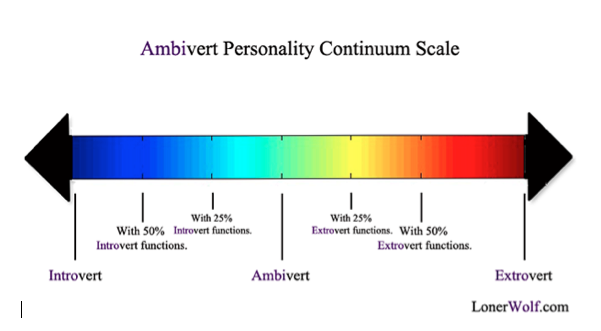 Extroverts Introverts And Ambiverts Collegiate Gateway
Extroverts Introverts And Ambiverts Collegiate Gateway
Extraversion tends to be manifested in.

Carl jung introversion and extraversion theory. CAPOBIANCO previously in Psychological Perspectives 202 1988 244-55. 26 July 1875 6 June 1961 was a Swiss psychiatrist and psychoanalyst who founded analytical psychologyJungs work has been influential in the fields of psychiatry anthropology archaeology literature philosophy and religious studiesJung worked as a research scientist at the famous Burghoelzli. Introvert and extravert basic personality types according to the theories of the 20th-century Swiss psychiatrist Carl Jung.
OPPOSITES and the first set is introversion and extraversion. Using the theory you can delve deeper into your own mind and comprehend your thoughts and feelings. The traits of extraversion or extroversion and introversion are a central dimension in some human personality theories.
The more obvious aspects of introversion are shyness a distaste for social functions and a love of privacy. Carl Jung Lexicon NYAAP Carl Jung on Extroversion Introversion is normally characterized by a hesitant reflective retiring nature that keeps itself to itself shrinks from objects is always slightly on the defensive and prefers to hide behind mistrustful scru-tiny. Extraversion tends to be manifested in outgoing talkative energetic behavior whereas introversion is.
After Jung came up with four dimensions for personality types Jung observed that Perceiving and Judging function were always used hand-in-hand with attitudes of Extraversion and Introversion. The terms introversion and extraversion were first popularized by Carl Jung although both the popular understanding and psychological usage differ from his original intent. Extreme extraversion can manifest in compulsive activity workaholism mania and addictive behaviors eg sex addiction serving the purpose of avoiding introversion or self-reflection at any cost.
Jungs theory on personality types shows the various behavioural patterns and attitude. Carl Jung Psychological Types CW 6 p. Jung and Freud on Introversion RICHARD M.
According to these theories an introvert is a person whose interest is generally directed inward toward his own feelings and thoughts in contrast to an extravert whose attention is directed toward other people and the outside world. He believed that extraverts direct their energy outwards - towards other people - and gain energy from such encounters. A stage of turning inward that has been described as.
In Psychological Types Jung described how extraverts engage with external stimuli Jung 1921. An Overview of Introversion and Extraversion Whereas the earlier classifications were based on observations of temperamental or emotional behaviour patterns Jungs model is concerned with the movement of psychic energy and the way in which one habitually or preferentially orients oneself in the world. INTROVERSION refers to a tendency to prefer the world inside oneself.
According to Jung there are two mutually exclusive attitudes extraversion and introversion. Extraversion is normally characterized by an outgoing candid and accommodating nature that adapts easily to. Rest of the four functions Sensing iNtuition Thinking and Feeling combine with two attitudes Extraversion and Introversion to form eight mental Functions-in-Attitude.
The trait of extraversionintroversion is a central dimension of human personality theories. We thus also avoid a possible misunderstanding namely that the thinking person is characterized by the absence of feeling and the feeling person by the absence of thinking. Jung believed that introversion and extraversion were present in everyone but that one attitude-type is invariably dominant.
Jungs typological constructs that have passed into general discourse albeit in varying interpretations. Foor consideration of the individual traits See extroversion and introversion. 244 By now it is well known that creativity requires incubation.
EXTRAVERSION the tendency to look to the outside world especially people for ones pleasures. When external factors are the prime motivating force for judgments perceptions affects and actions we have an extraverted attitude or type. Extraversion is characterized by a desire to influence and be influenced by events a need to join in and get with it the capacity to endure bustle and noise of every kindthe cultivation of friends and acquaintances none too carefully selectedHe has no secrets he has not long since shared with others.
If you have taken a Myers-Briggs Personality Test this is a concerned observers explanation of the concepts behind it. Carl Gustav Jung originally Karl Gustav Jung j ʊ ŋ YUUNG. Extraversion and introversion were popularised by Swiss psychoanalyst Carl Jung 1875-1961 in 1921.
Page numbers in the original publication are given in the text in brackets. The terms introversion and extraversion were introduced into psychology by Carl Jung although both the popular understanding and current psychological usage vary.